Is Forex Trading Halal or Haram? A Complete Islamic Finance Guide for Traders
The same question is asked by all Muslims worldwide, “Is forex trading halal or haram?’’
Some scholars suggest it's gambling money, so it’s haram, and other scholars say it’s halal.
The Forex market offers numerous opportunities to participants, and understanding what aligns with Islamic Banking and Finance principles is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unpack the core Islamic teachings around trading, the practicalities of forex, and how Muslim traders can sail the market while staying true to their faith.
Introduction to Islamic Finance and Forex Trading
With 6 trillion US dollars in daily volume, the foreign exchange market is the largest.
It's where traders are able to buy and sell different currencies to make a profit from the fluctuations in the exchange rates.
The market is open 24 hours a day and 5 days a week, which offers unimaginable liquidity and opportunities for traders.
However, for Muslims, the question “Is online forex trading halal or haram?” goes beyond profit potential.
Islamic finance principles emphasize fairness, transparency, and avoiding riba (interest) and gharar (excessive uncertainty or speculation).
These rules aim to ensure that financial dealings are ethical, avoid exploitation, promote social justice, and do not diminish human dignity.
For Muslim traders, before entering any sort of trade or deal, these principles are in mind.
But keep in mind that not all forex trading practices are created equal, and understanding the differences is a necessity.
Key Principles of Halal Trading
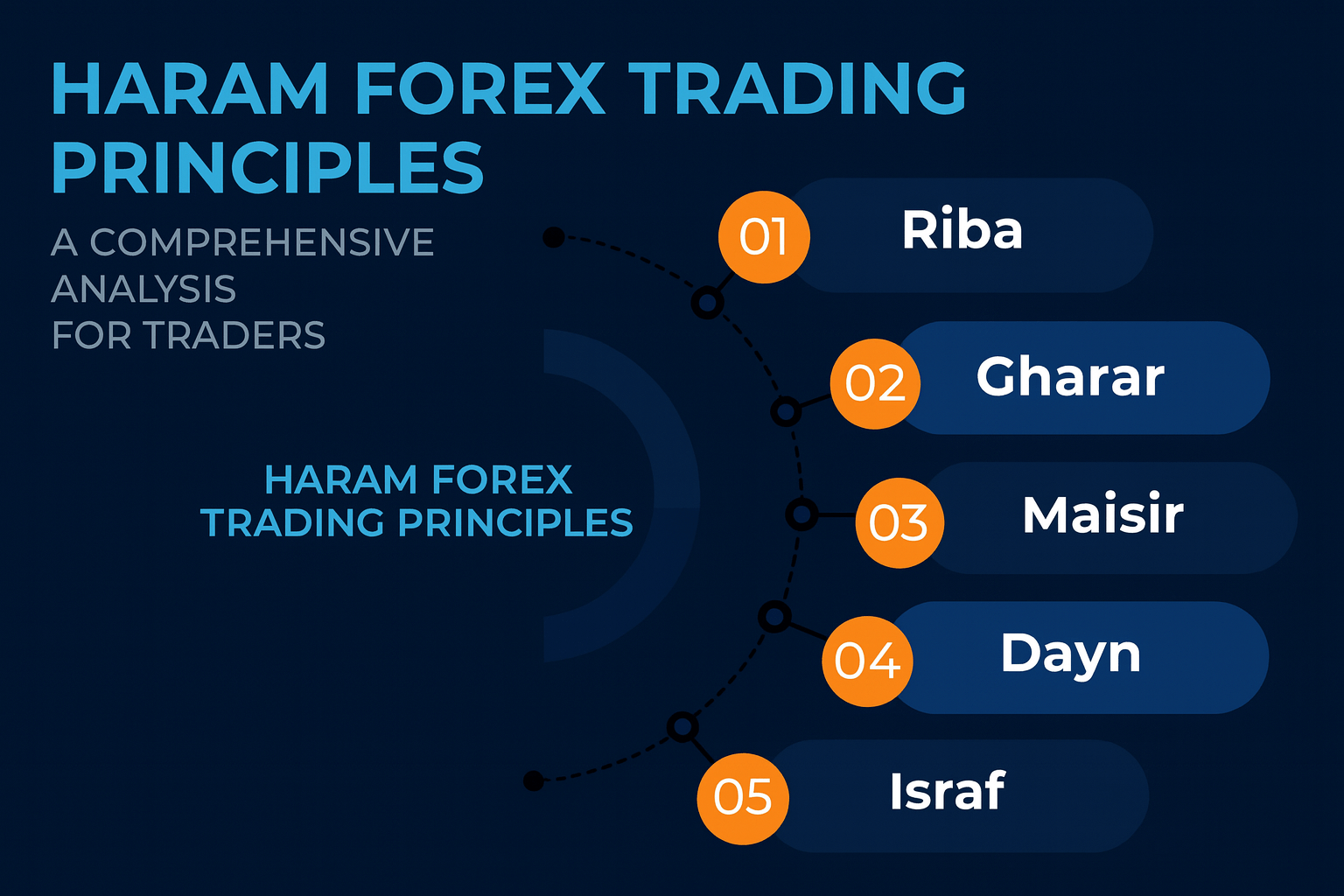
Avoidance of Riba and Gharar
The core and most well-known prohibition in Islamic finance is riba, which is commonly understood as usury or interest.
Any transaction between two parties or more that involves guaranteed interest paid or received is considered haram (forbidden) as it promotes unjust enrichment without an actual economic activity.
In forex trading, this often translates to the interest charged on overnight positions, known as swap fees.
Muslim traders who want to keep their trading halal must avoid these interest-based transactions entirely.
An equally important and respected concept is gharar, which refers to excessive uncertainty or ambiguity in contracts, which is close to the concept of gambling.
Islamic law forbids transactions where outcomes are uncertain or the terms are unclear, as this can lead to exploitation and unfairness.
Gharar is especially relevant in highly speculative trading practices, where the risks are disproportionate or unknown, which sets an unjust probability of a gain or loss.
Halal forex trading requires strict adherence to these principles, often facilitated through swap-free or Islamic accounts.
These accounts remove any interest charges and are designed to comply fully with Sharia guidelines, helping traders avoid both riba and gharar.
Beyond these prohibitions, Islamic finance emphasizes fairness, transparency, and ethical responsibility.
All financial transactions should be clear, equitable, and promote genuine economic activity rather than mere speculation.
Real Economic Activity and Fair Trading Practices

One of the cornerstones of halal trading is that it must be rooted in real economic activity.
This means trading should reflect the genuine exchange of goods, services, or assets with intrinsic value.
Rather than speculative bets or paper transactions that have no tangible or physical backing.
In foreign exchange markets, this expresses spot trading, where an actual currency exchange occurs and ownership is transferred from one party to another.
Unlike derivative products (Futures, Options, CFDs), which lack direct ownership of an asset and might involve speculative contracts.
Fair trading practices are essential to halal forex trading.
This includes having transparent, well-defined contracts that clearly state terms and conditions, avoiding deceptive or manipulative practices that could mislead one party or create unfair advantages.
Islamic trading accounts and brokers offering Islamic forex accounts have the most responsibilities here.
These accounts are specifically structured to ensure transparency, fairness, and, of course, compliance with Sharia law.
Traders using these accounts are equipped to engage with the market ethically and within a halal range, reducing the risks associated with speculation and unfair dealings.
Additionally, employing technical analysis and disciplined risk management strategies empowers traders to make informed, calculated decisions.
This minimizes unnecessary risk-taking (Gharar) and aligns with Islamic teachings.
Forex Trading and Islamic Principles

Forex Trading Haram and Prohibited Practices
Certain practices within forex trading are widely considered haram under Islamic law.
One of the most commonly flagged issues is the payment or receipt of interest on overnight positions (swap/rollover fees).
Such transactions are a clear form of riba (usury or interest) and are thus forbidden.
Moreover, speculative transactions that amount to gambling or excessive, unnecessary risk-taking are also prohibited.
Islamic finance encourages risk-sharing and discourages activities that resemble gambling, where the outcomes are purely chance-based without underlying economic value.
Trading instruments like Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are typically viewed as haram because they represent derivatives where the trader does not own the underlying asset, making them speculative and often tied to interest.
Another concern is the use of high leverage, which magnifies exposure and risk disproportionately.
Islamic principles advocate for moderation and caution, so excessive leverage that can lead to reckless trading is discouraged or considered non-compliant.
To tackle these issues, many Muslim traders rely on swap-free accounts and avoid carry trading strategies, which rely heavily on interest rate differentials and are thus not permissible.
Sharia Law and Regulatory Environment

The permissibility of forex trading under Islamic law is subject to interpretation by various Islamic scholars and depends on how trading practices align with Sharia principles.
While many scholars agree that forex trading can be halal when conducted correctly, opinions vary regarding specific products and methods, based on the fatwa and the religious school they follow (Hanafi, Shafi’i, Jaafari, Maliki, Hanbali).
Furthermore, regulatory environments in Islamic countries or regions with Sharia-compliant financial systems may impose rules that reflect these religious guidelines.
Different Islamic countries have different regulations that allow only Sharia-compliant market participation practices, while other non-Islamic countries follow the general financial laws that require traders to practice with caution and care.
Muslims must ensure that their trading activities are aligned with religious rulings and legal frameworks as well.
So, selecting brokers that are registered and have never participated in any shady activities is a necessity before ensuring that they offer Islamic accounts that use halal trading instruments.
The legalities of forex trading vary worldwide.
Some countries impose strict restrictions or outright bans on retail forex trading due to regulatory concerns, while others allow it under regulated environments.
Traders should stay informed about their local laws and choose brokers and trading strategies that align with both Sharia principles and legal requirements.
Types of Trading and Investment: What’s Halal and Haram?
CFD trading, or Contracts for Difference, involves speculating on the price movements of financial assets such as stocks, indices, or commodities without actually owning the underlying asset.
On the surface, it may seem like a convenient, flexible way to trade markets, but from an Islamic perspective, CFDs raise several serious red flags.
Why CFDs Are Typically Haram
Most scholars agree that CFD trading is generally haram due to three key violations of Islamic financial ethics:
- No Real Asset Ownership: Islamic finance emphasizes tangible economic activity. With CFDs, you never actually own the asset you're trading. You're merely entering a contract to benefit from price fluctuations; this speculative nature closely resembles gambling (maysir), which is strictly forbidden.
- Presence of Riba (Interest): Most CFD platforms involve overnight fees or rollover charges, which are essentially interest payments. Even if the trader tries to close positions quickly, interest may still be incurred under specific conditions, automatically rendering the trade non-compliant.
- Excessive Gharar (Uncertainty): CFDs are inherently volatile and complex. The terms of these contracts can be vague, and the pricing mechanisms are often manipulated through leverage and artificial spreads. This introduces an element of excessive uncertainty, or gharar, which Islamic law strictly prohibits in contracts.
Swing Trading and Forex Trading as Halal Strategies

While many modern trading strategies border on speculation, some can be halal-compliant if structured correctly, especially swing trading and spot forex trading.
Swing trading involves holding a position in a financial instrument for several hours, days, or even weeks
Usually based on technical analysis and medium-term market trends.
It’s far less aggressive than day trading or scalping and can be halal under the right conditions:
- No Interest (riba): Ensure no swap or overnight interest fees are incurred.
- Proper Ownership: The trade should involve real ownership of the asset or currency.
- Controlled Risk: Use of disciplined stop-losses and risk management avoids the element of maysir (gambling).
Forex Spot Trading: Permissible with Caution
Forex trading is a hotly debated area in Islamic finance.
However, spot forex trading, the immediate buying and selling of currency pairs, is generally viewed as halal if the transaction is conducted according to Sharia guidelines.
Key conditions for halal forex trading:
- Immediate Settlement (T+0): Both the buying and selling should occur on the spot without delay.
- No Leverage with Interest: Avoid using margin accounts that incur interest (riba).
- Transparent and Fair: The terms of the trade must be clear, and the broker should not manipulate pricing.
Creating a Halal Forex Trading Account

No solution fits all, especially when it comes to what is halal and haram.
To bridge the gap between modern trading platforms and Islamic financial ethics, many brokers now offer what’s called an Islamic Forex Account.
Features of Islamic Forex Accounts
A properly structured halal trading account should:
- Eliminate Interest (Riba-Free): The most critical feature is the removal of all swap or rollover charges that resemble interest payments.
- Ensure Full Transparency: All fees, spreads, and contract terms must be clear and disclosed upfront. Hidden commissions or arbitrary charges are unethical and violate Islamic principles.
- Use Ethical Trading Practices: The trading platform should operate with integrity, offering real-time execution, stable infrastructure, and fair dealing.
- Avoid Speculative Instruments: Islamic accounts should not allow trading in instruments that are inherently haram, such as CFDs, futures, options, or highly leveraged products.
Selecting the Right Broker
Unfortunately, not all “Islamic accounts” are genuinely Islamic. Some brokers use the label purely for marketing while still applying indirect interest or questionable fee structures.
When choosing a halal trading platform, make sure to:
- Verify Fatwa Certification: Check whether the account is backed by a credible Sharia advisory board.
- Review the Fee Structure: Avoid brokers that charge “admin fees” as a hidden form of interest.
- Check Regulatory Oversight: Look for platforms licensed by respected financial regulators, such as FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), or DFSA (UAE).
Ultimately, your broker should be transparent, compliant, and ethically aligned with Islamic financial values, not just using Islamic terms for branding.
Conclusion
Sailing in the financial markets as a Muslim trader involves more responsibility than the average trader.
As it requires aligning your trading with Islamic ethical and financial principles.
Understanding the difference between halal and haram practices in forex trading empowers you to trade confidently and responsibly.
Whether you’re asking, “Is forex trading halal or haram?”, “Is online forex trading halal or haram?”, or “Is currency trading halal or haram?” The answer depends on your approach.
By avoiding interest, excessive speculation, and ensuring fairness, forex trading can be a halal way to engage with global financial markets.
Always combine your trading activities with continuous education, ethical awareness, and, if possible, guidance from Islamic finance scholars to stay on the right path.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is forex trading halal or haram?
A: Forex trading can be halal if done without interest (riba) and excessive speculation (gharar), typically through swap-free Islamic accounts.
Q: Are online forex trading platforms suitable for Muslim traders?
A: Yes, many platforms offer Islamic accounts designed to comply with Sharia principles, eliminating interest charges and offering ethical trading terms.
Q: Is currency trading halal or haram if it involves leverage?
A: Excessive leverage that leads to speculative risk is generally discouraged or considered haram in Islamic finance. It may be permissible if used cautiously and without riba.
Q: Can swing trading be halal?
A: Yes, swing trading focusing on real currency exchange without interest and excessive uncertainty can align with halal principles.
Q: Are cryptocurrencies halal for trading and investment?
A: Opinions differ among scholars. Some view cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin as halal due to their utility and decentralized nature, while others consider them haram because of volatility and speculative use.
Q: What makes an Islamic trading account truly halal?
A: A genuinely halal account must eliminate all forms of interest (swap/rollover fees), avoid excessive risk, and clearly disclose all fees and terms without hidden costs or unethical instruments.
Q: Is day trading considered halal in Islam?
A: Day trading may be permissible if it involves real asset ownership, no riba, and transactions are settled immediately. However, its fast-paced, speculative nature often raises concerns and requires caution.
Take Your Trading to Next Level
Take Your Trading to Next Level
You Might Also Like:

